Answers to Assignment 2, Chapter 2
OCG123, Spring 2001
Review Questions
1. If a perturbation that decreases component A also decreases component B, the
two components are coupled positively.
2. A feedback loop is a "round trip" connection between two components such that each affects the other.
3. Negative feedback loops diminish the effect of disturbances because the second component always acts back on the first component in the opposite way in which it first changed. Thus no matter how the first component changed, the second component changes it back in the direction of its original state, i.e., reduces its disturbance.
4. A perturbation is a short-term disturbance of of a system, whereas a forcing is a longer-term disturbance.
5. Some equilibrium states are stable; others are unstable. It depends on whether the state is at a minimum or a maximum of energy.
6. The albedo of a system is its fractional reflectance of some wavelength of electromagnetic radiation. The earth's albedo affects climate because the higher the albedo, the less solar radiation is available to warm the earth.
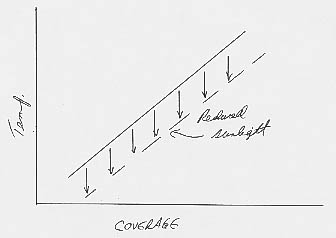
7. Daisies on Daisyworld regulate its temperature by growing and reflecting more radiation (increasing the albedo) or by dying off and reflecting less radiation (increasing the albedo).
Critical-Thinking Problems
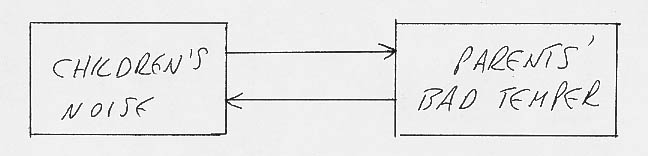
1. a. The system diagram for the Dysfunctional family is:

b. The feedback loop is positive because each component
(parent and children) affects the other positively.
c. This makes the family unstable. That is why they are named
the "Dysfunctia" family.
2. a. The relations to appear on the system diagram are (1) photosynthesis affecting CO2, (2) CO2 affecting temperature, (3) CO2 affecting photosynthesis, and (4) temperature affecting photosynthesis. These effects are negative, positive, positive, and negative, respectively. The resulting system diagram is:
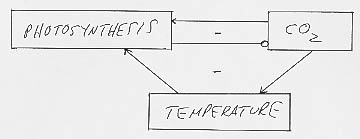
b. There are two feedback loops, one between
photosynthesis and CO2, and the other between photosynthesis, CO2,
and temperature.
c. Both feedback loops are negative. (Thank goodness!)
d. (i) An increase in CO2 will increase the
photosynthesis via the upper loop and increase it via temperature in the lower
loop. The increased rate of photosynthesis will then reduce the CO2
via the negative connection in the upper loop. The net effect will be little or
no change in the system. (ii) A decrease in temperature will decrease the
photosynthesis, which will then increase the CO2 and the temperature
again. The increased CO2 will also increase the photosynthesis to
offset the effect of the first loop. Again the net effect will be little or no
change in the system.
e. A steady increase in solar luminosity with time will
3. a. An increase in black daisies will decrease the albedo and warm the planet.
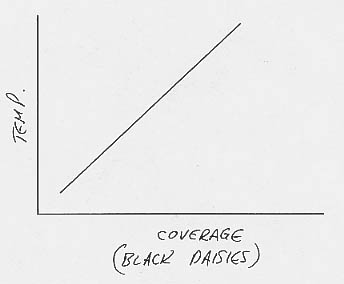
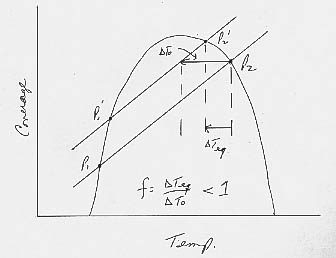
b. Assuming that the black daisies grow best at intermediate temperatures just like the white daisies, the stability diagram for a planet with black daisies will have the same parabola as with white daisies, but an albedo line with a positive slope instead of a negative slope:
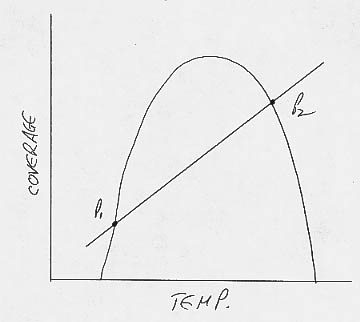
c. As before, the higher equilibrium state is stable. This time, however, it is at higher temperatures rather than lower temperatures.:
d. See (c).
e. A decrease in solar luminosity would shift the albedo
line to the left (see graph below). This would decrease the feedback factor f.
f. The feedback factor is less than one.
Scoring: Two points for each review question; four for each critical-thinking problem. Total score scaled to a maximum of ten.