Homework 3 Answers Chapter 4 20 points
Define (1 point each):
Hadley circulation
The
process by which an air mass undergoes convergence at the tropics and divergence
at about 30N or 30S latitude in one convection cell.
Obliquity
The angle of a planet’s spin axis relative to a line drawn perpendicular to the plane of the planet’s orbit around the sun; tilt.
Latent heat of vaporization
The energy required to effect a change of phase between a liquid and a gas. Converting a liquid to a gas requires an addition of energy; converting a liquid to a gas releases energy to the environment.
Latent heat of fusion
The energy required to effect a change of phase between a solid and a liquid. Converting a solid to a liquid requires an addition of energy; converting a liquid to a solid releases energy to the environment.
Fill in the blanks of the modified Figure 4-21 (below) (2points):
![]()
![]() Energy
( Absorbed)
)
Energy
( Absorbed)
)
![]()
__sublimination____
___melting___________ ___evaporation_____
![]()
![]()

____solid_____ __liquid_____ _____gas____
![]()
![]()
_____freezing_______ _____condensation_____
_____deposition_____
![]()
![]()
![]() Energy
( Released )
Energy
( Released )
Review Questions (1, 3, 5) 2 points each
1. The two main functions of the global circulation systems are:
a.___Thermal balance____ which is maintained by…
transporting energy from the equatorial regions, where it is in excess, to the polar regions, where there is a deficit.
b.__ Chemical balance____ which is maintained by…
removing chemicals, particularly waste products, from their source regions to sinks.
3. a. see Figure 4-4 (something
close to below)
net radiation surplus
![]()

![]() Energy
Energy
![]()
![]() absorbed
absorbed
![]()
![]() emitted
emitted
Net radiation deficit
![]()
90 South 0 North 90
Latitude
b. There is a ___surplus____ near the equator and a _deficit______ near the poles.
c. This distribution is important because it forces the earth to set up a circulatory pattern that moves energy from the equator to the poles.
5.a. see Figure 4-6
b. The Hadley circulation changes seasonally because the ITCZ moves north and south with the seasons. See Figure 4-15 and 4-16 for visual (not necessary for full credit).
(extra info #9 next page) The Southeast Asian monsoon is driven largely by conditions on the Tibetan Plateau—the low pressures and strong convection in summer (which pulls moist air northward from the Indian Ocean) and the low temperatures, extensive snow cover, and high pressures of winter (which push cold, dry air southward over India and Southeast Asia).
9.Draw processes of the SE Asian monsoon (see Figure 4-19 for arrows) Please make your arrows visible (use marker or different color pen). (4 points)
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
Dry High High

What are the 3 major reservoirs of water on Earth? What percentage of water is in each?
Fill in the blanks. (4 points)
1.The _oceans_______ contains __97__% of the water on earth in the form of seawater.
2.The _atmosphere________ contains less than __0.001__% of the water on earth in the form of water vapor.
3. Land contains about ___3__% of the water on earth. The land surface, in the forms of
ice sheets, glaciers, snow, lakes, and rivers, and the land subsurface, in the form of _groundwater__________. (there was an extra space here – sorry!)
One percent of all water found on land (or 0.03% of global water) is stored in _rivers_______, __lakes______, and soil.
About three-fourths of all water found on land (or _2.25_% of global water) is found in
polar ice sheets and about one-fourth (or 0.75% of global water) is found as groundwater.
Ch 4 Critical Thinking - Extra Credit (5 points)
2. a.b.The 2 feedback loops are intertwined as shown below. They are both negative.
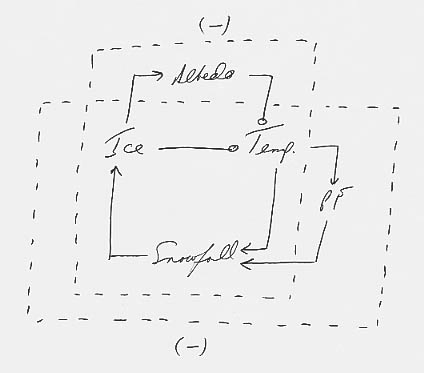
c. The negative feedback loops imply that ice sheets are stable with respect to
disturbances. That means that they will not necessarily grow or shrink of their
own accord—they
will require prolonged external forcings.