 |
|||||
 |
 |
||||
OCG123 Lab 2-Atmospheric Circulation and Coriolis Effect
Quiz
1. Answer the following by circling the correct response.
a. Liquid water changes to water vapor by the process called (condensation, evaporation, deposition).
b. (Warm, Cold) air has the greater water vapor capacity.
c. The heat capacity of water is (higher, lower) than that of the land.
d. Wind blows (from high pressure to low pressure, from low pressure to high pressure).
e. When condensation occurs, heat is (absorbed, released) by water vapor.
f. Rising air (warms, cools) by (expansion, compression).
g. The direction of the surface velocity of the earth is (east, west).
h. The coriolis effect is the (highest, lowest) at the equator.
i. If the Earth rotates faster, the Coriolis effect will be (larger, smaller).
2. The net radiation (the difference between the incoming solar radiation and the outgoing terrestrial radiation) is not the same at each latitude. What are the two most important processes that try to equalize them?
atmospheric and oceanic circulation
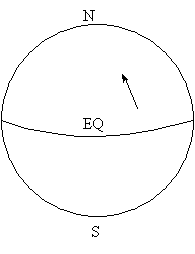
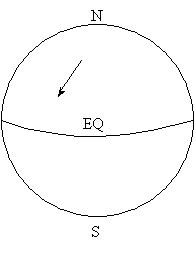
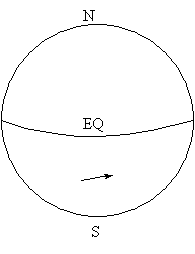
3. Sketch the direction that each air parcel below would be deflected from its initial path by the Coriolis effect.
 |
|||||
 |
 |
||||